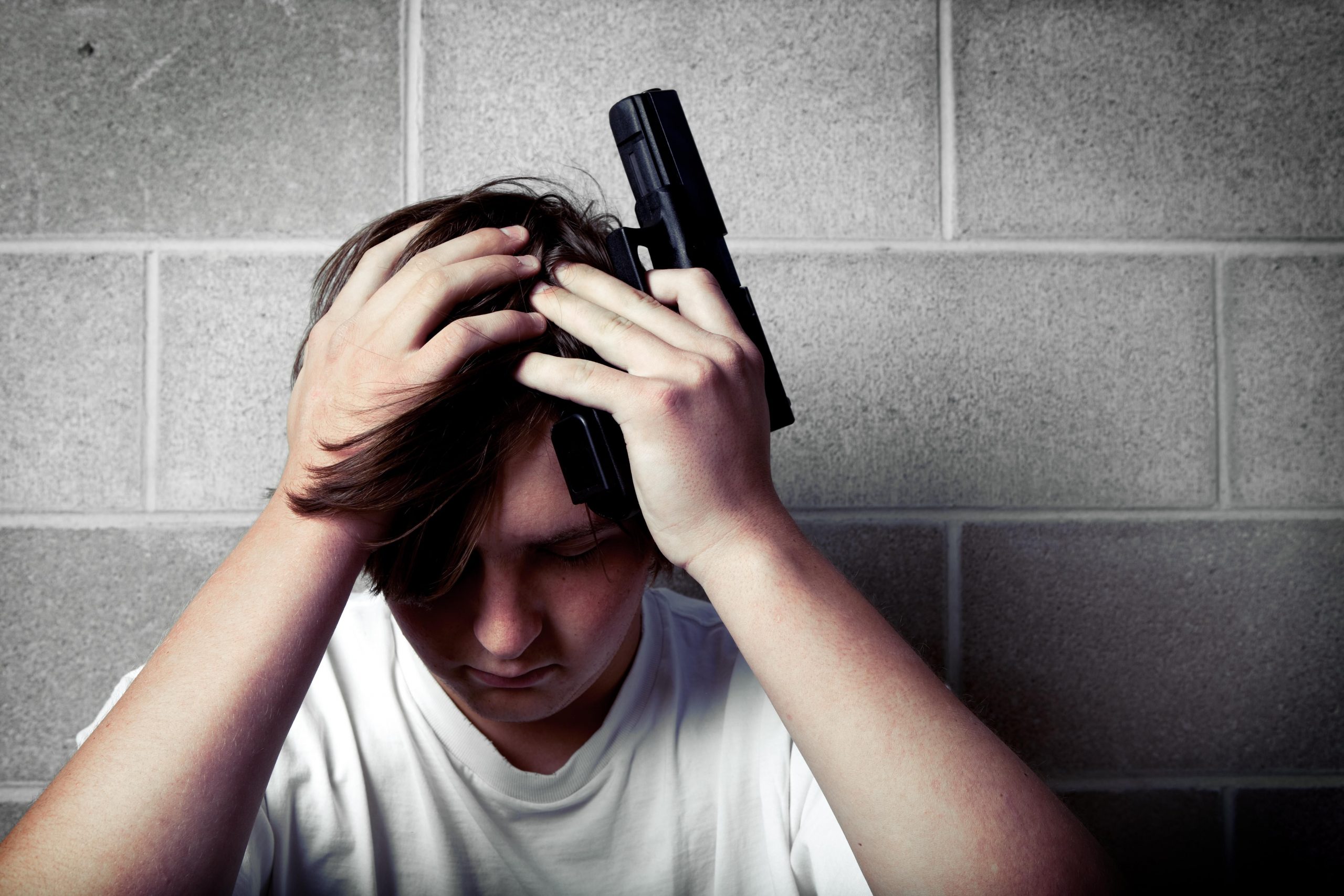
If you think teen gun violence is not a pressing issue, a new study suggests otherwise. Researchers found the percentage of U.S. teenagers carrying handguns has risen by 41% over the past two decades — with notable increases seen among white teens from higher-income families. The researchers tracked handgun carriage among 12- to 17-year-olds between… read on > read on >