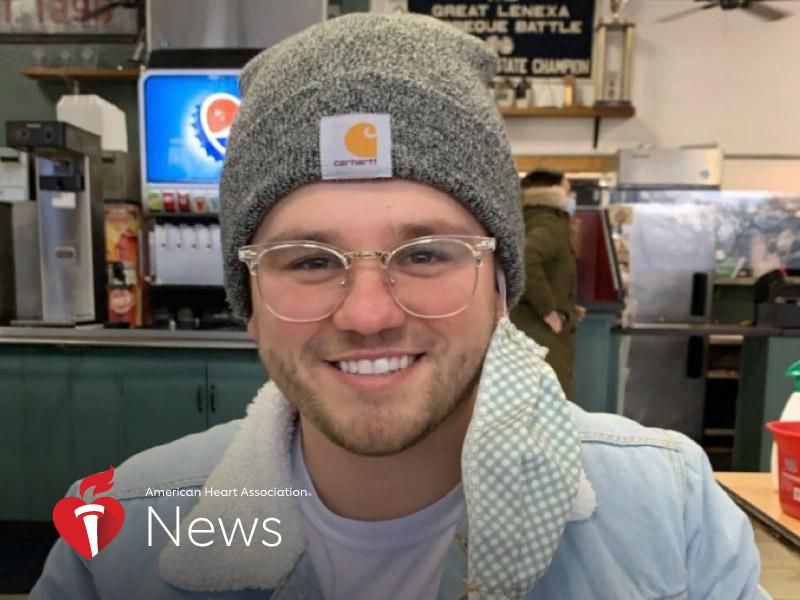
THURSDAY, May 27, 2021 (American Heart Association News) — Soon after turning 21, Jacob York and his buddies from the University of Missouri were in Miami Beach, Florida, for spring break. They spent their days by the shore and nights at the bar. So when he felt an incredibly sore throat and a headache, he… read on > read on >