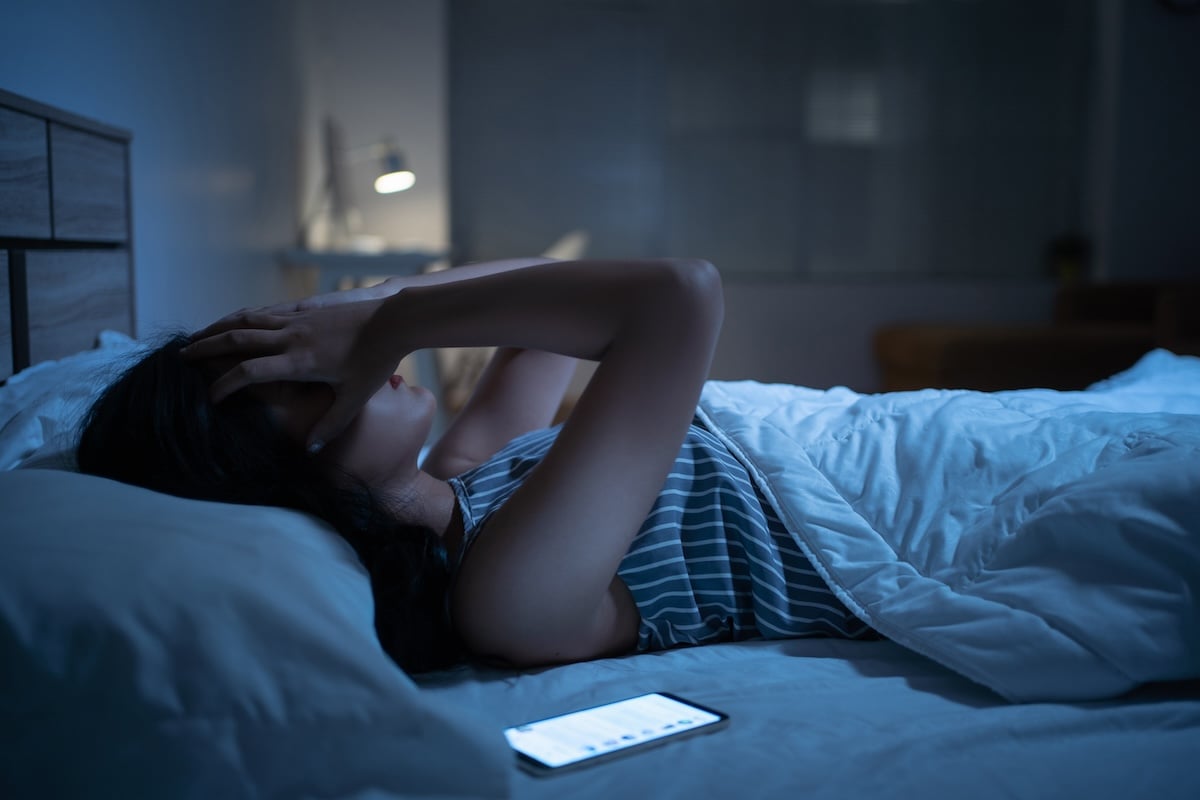
Many young adults are experimenting with “bed rotting” and other sleep trends that have gone viral on TikTok and other social media platforms, a new poll shows. Sleep experts say these trends likely won’t do any immediate harm, but they add that people would do better to see a doctor if they’re not getting adequate… read on > read on >











.jpg)