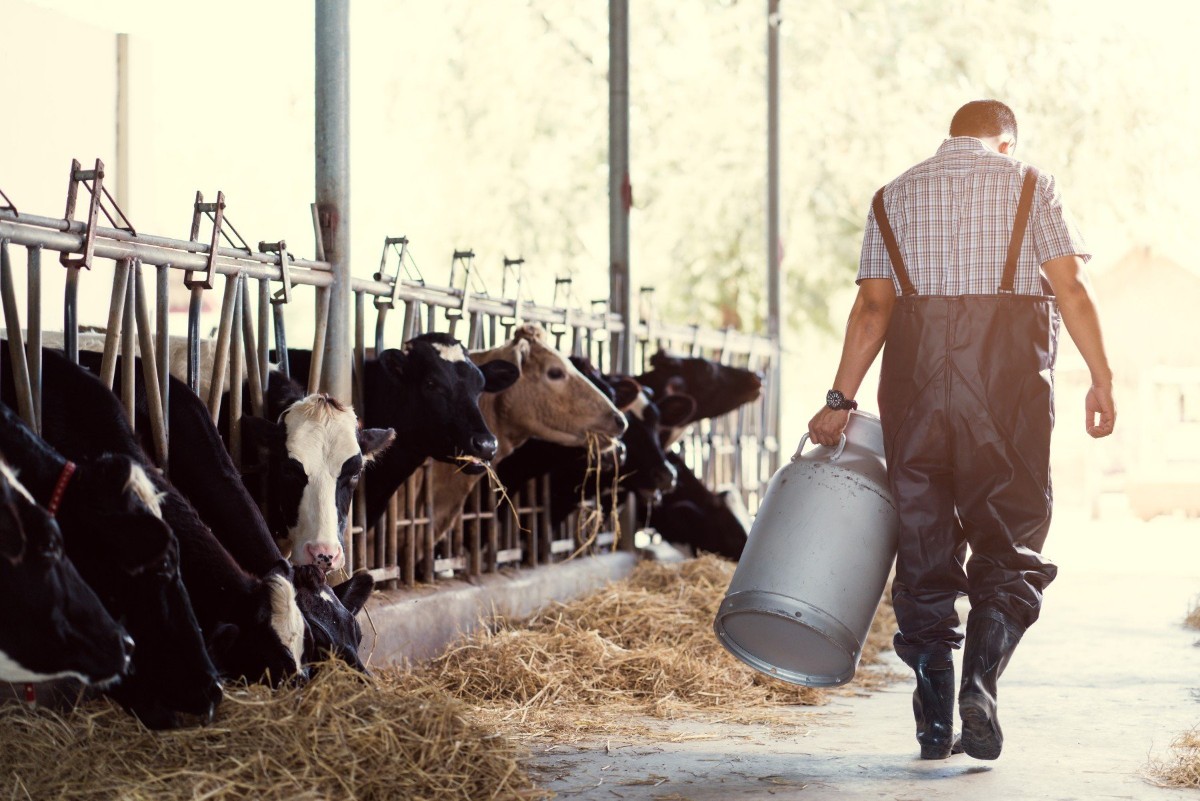
As bird flu continues to spread among U.S. dairy cows, reassuring new government research finds the pasteurization process widely used in the industry effectively kills all bird flu virus in milk. In a health update posted Friday, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) said the results are the latest to show that pasteurized grocery store milk remains… read on > read on >