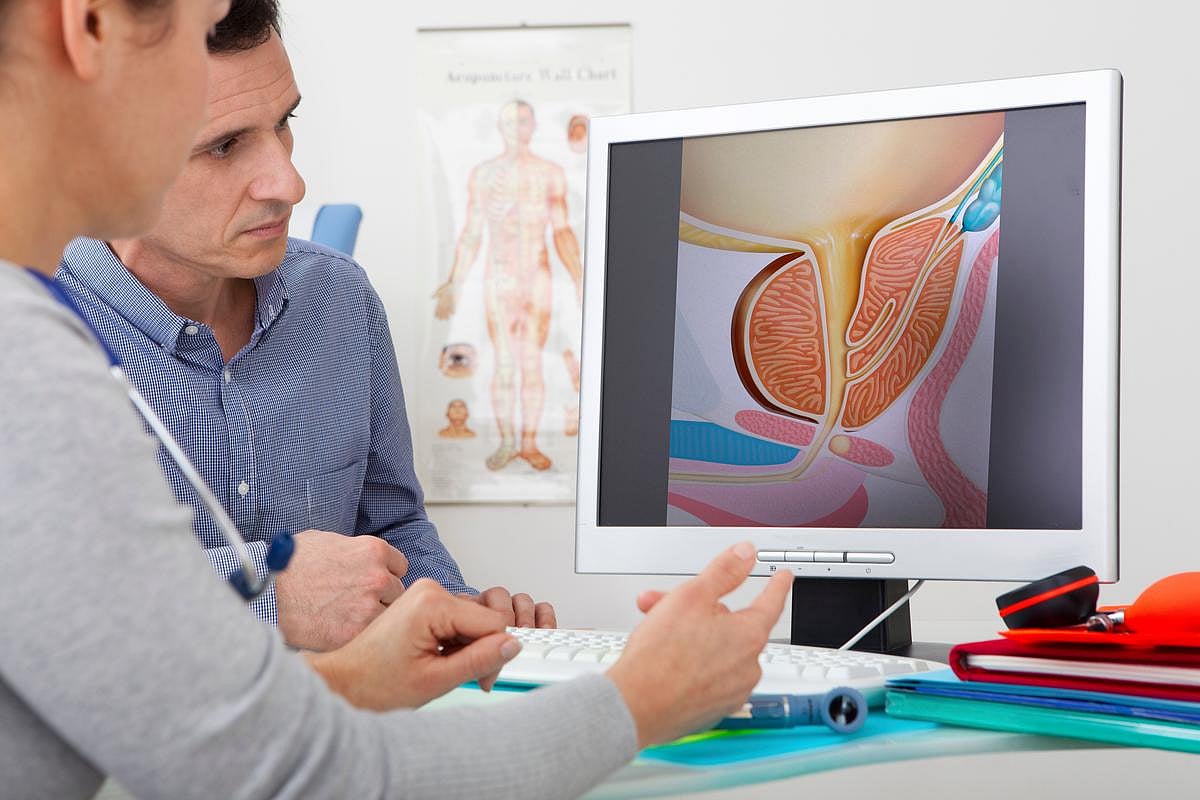
You may have seen recent news stories reporting that a national data investigation found that routine childhood vaccination is slipping across much of the United States, leaving classrooms and daycares with growing gaps in protection against highly contagious diseases like measles and whooping cough. That’s a warning sign for every family with children — and… read on > read on >