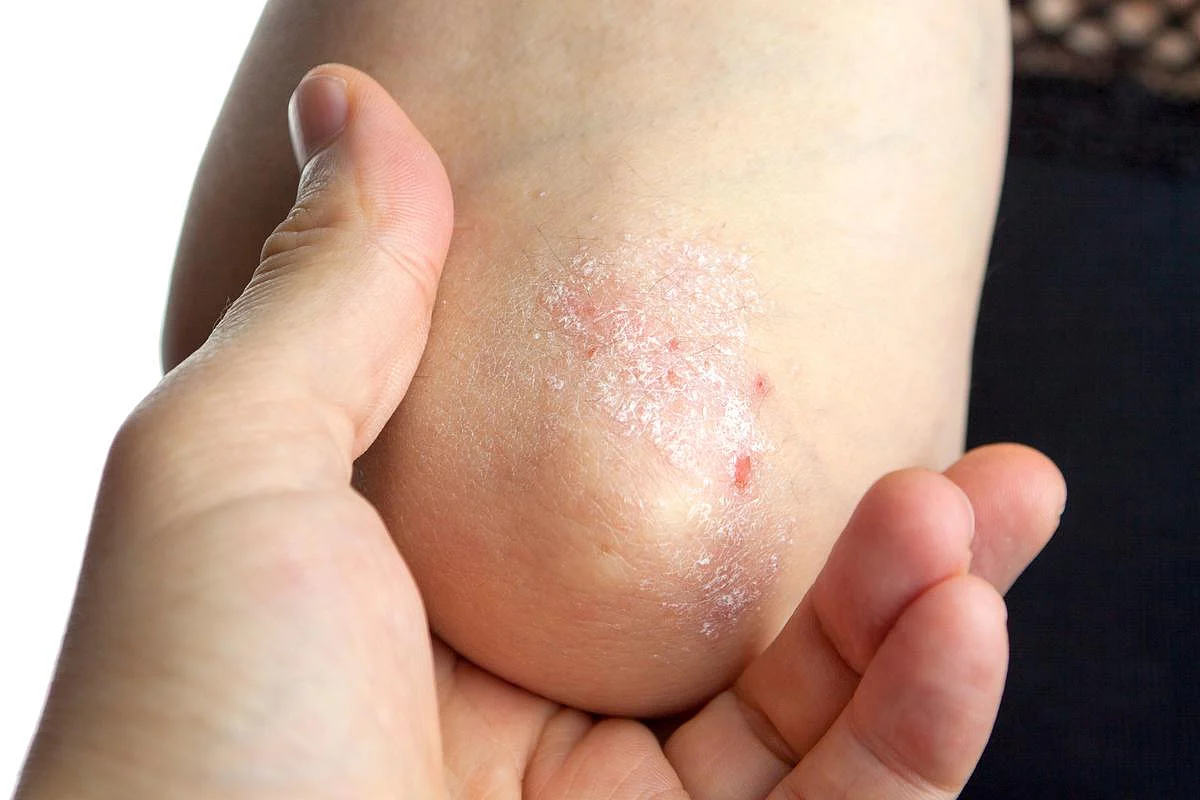
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that mainly affects the skin. When you have psoriasis, your immune system sends signals to your skin cells to grow too fast. Normally, skin cells take about a month to form and rise to the surface. In people with psoriasis, this process happens in just a few days. Because… read on > read on >












.jpg)

















