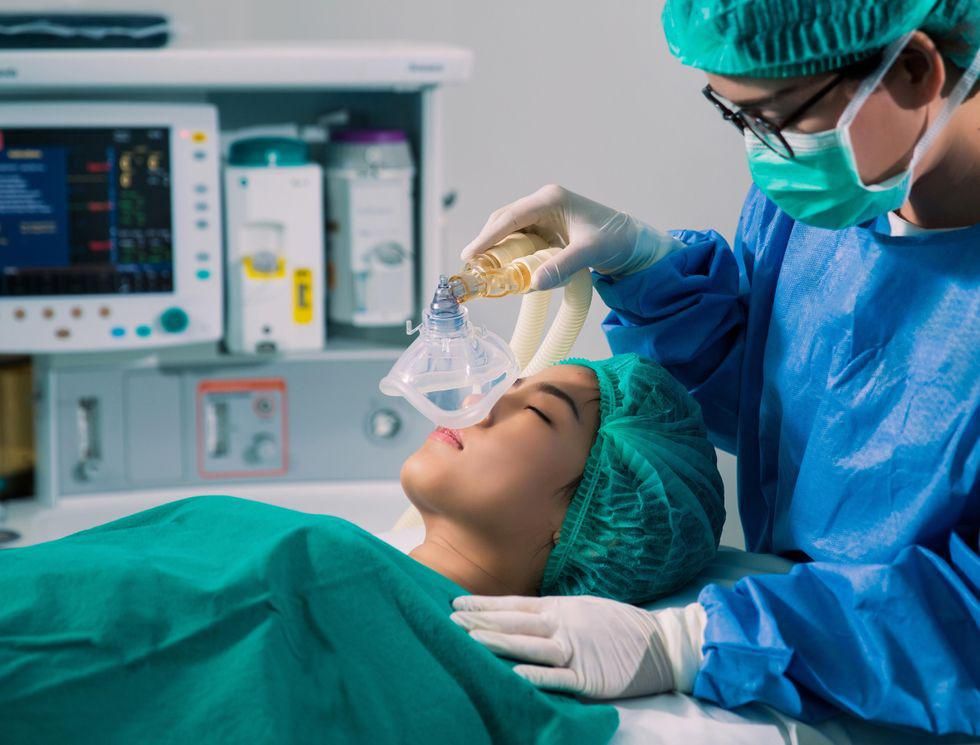
Routine face mask ventilation during an operation doesn’t increase the surgical team’s risk of coronavirus infection, according to a new study. Face mask ventilation is typically used for surgical patients under general anesthesia. However, its designation as an “aerosol-generating procedure” by the World Health Organization has altered operating room procedures and efficiency during the COVID-19… read on > read on >