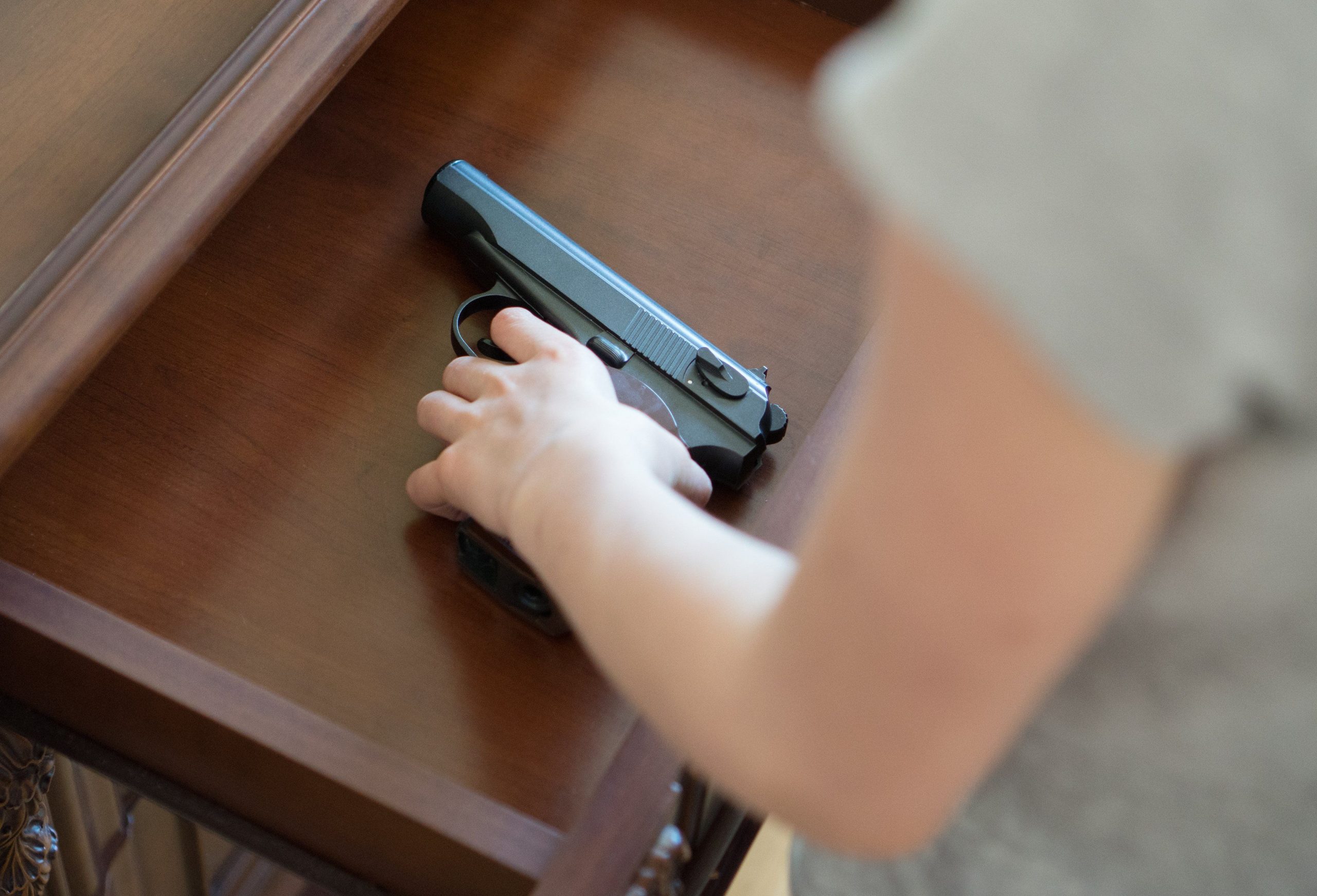
America’s kids are safer now than a decade ago when it comes to many types of injury, with two glaring exceptions: drugs and guns. That’s the crux of a new study that looked at injury trends among U.S. children and teenagers between 2011 and 2021. It found that nonfatal injuries from accidents and assaults fell… read on > read on >