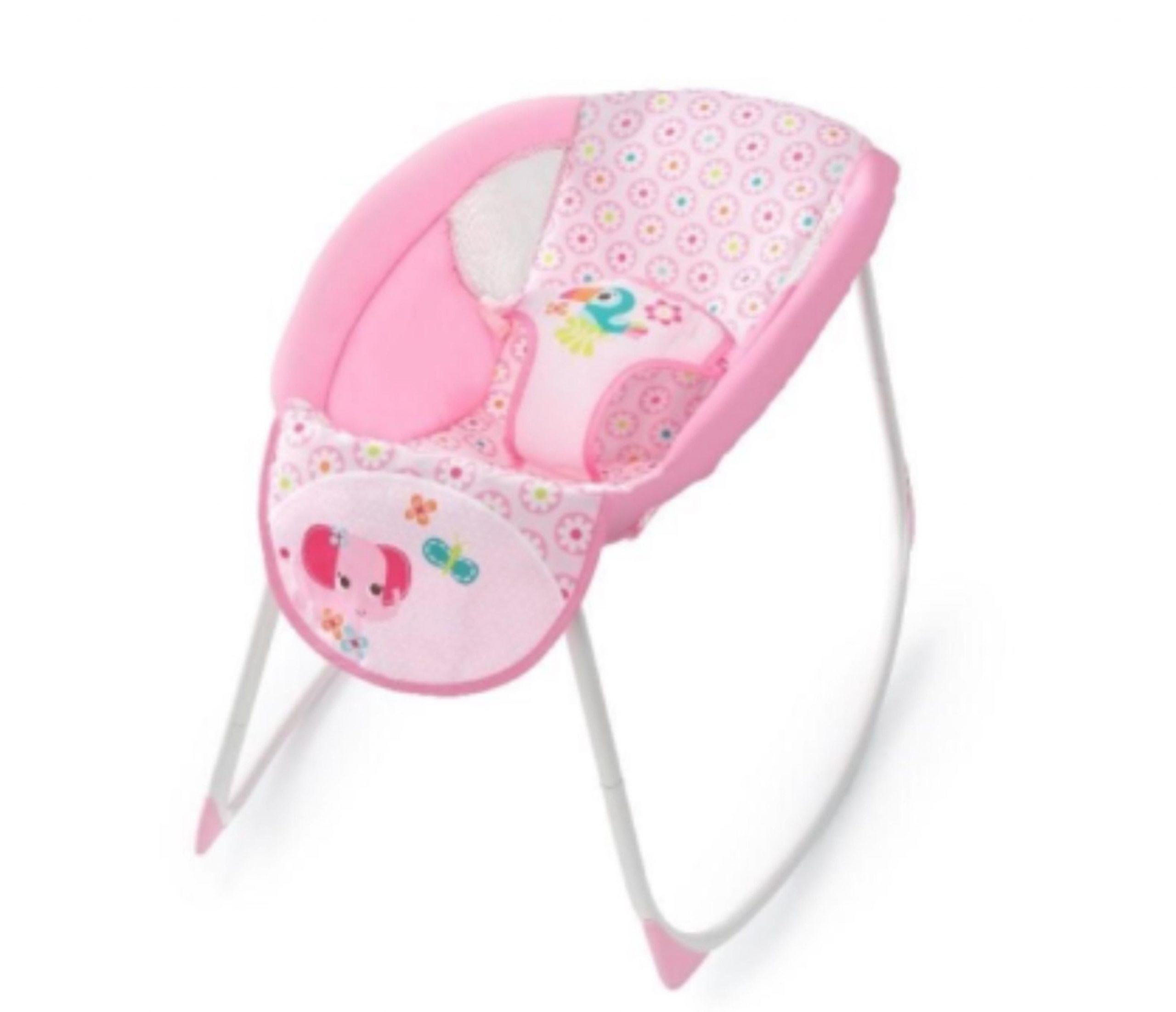
Following the deaths of 15 infants, families are advised to immediately stop using all models of Kids2 Rocking Sleepers, according to a second recall notice. Four of those 15 babies died after the first recall notice, the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) reported. The company is recalling 694,000 Rocking Sleepers. Parents can contact the… read on > read on >