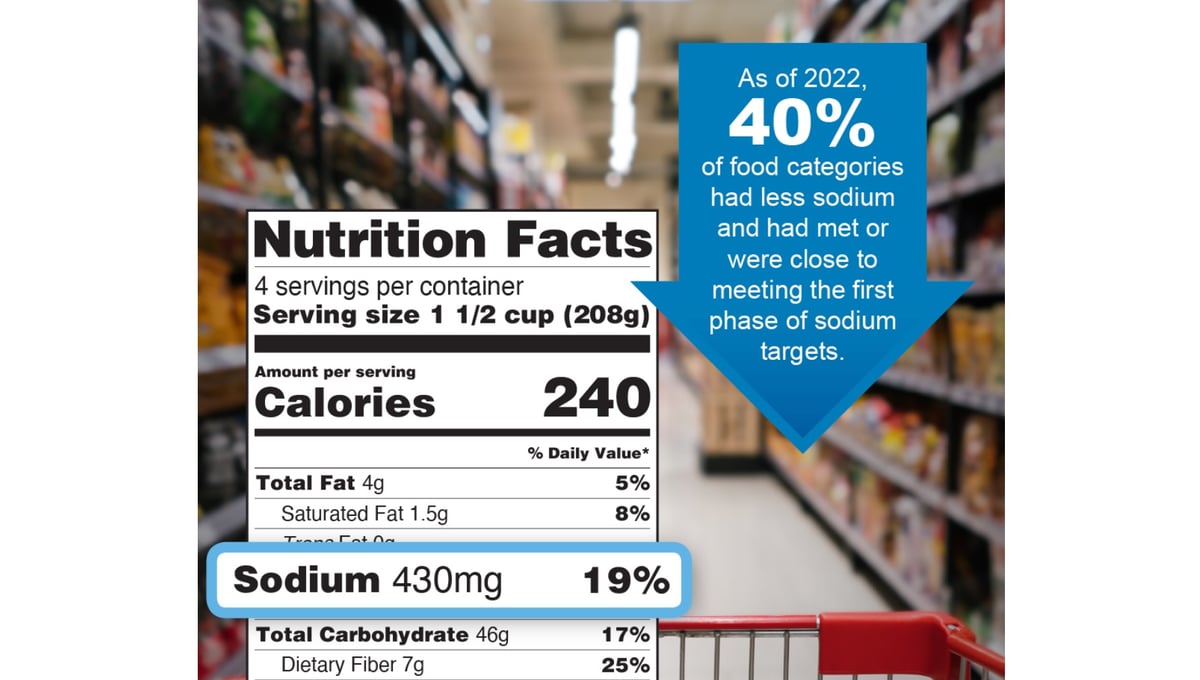
Emboldened by success in its initial efforts to cut dietary salt intake by Americans, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on Thursday announced Phase II of the endeavor. U.S. Dietary Guidelines recommend that a person consume no more than 2,300 milligrams (mg) of sodium per day, the equivalent of about one teaspoon of salt. Excess… read on > read on >












.jpeg)



.jpg)













