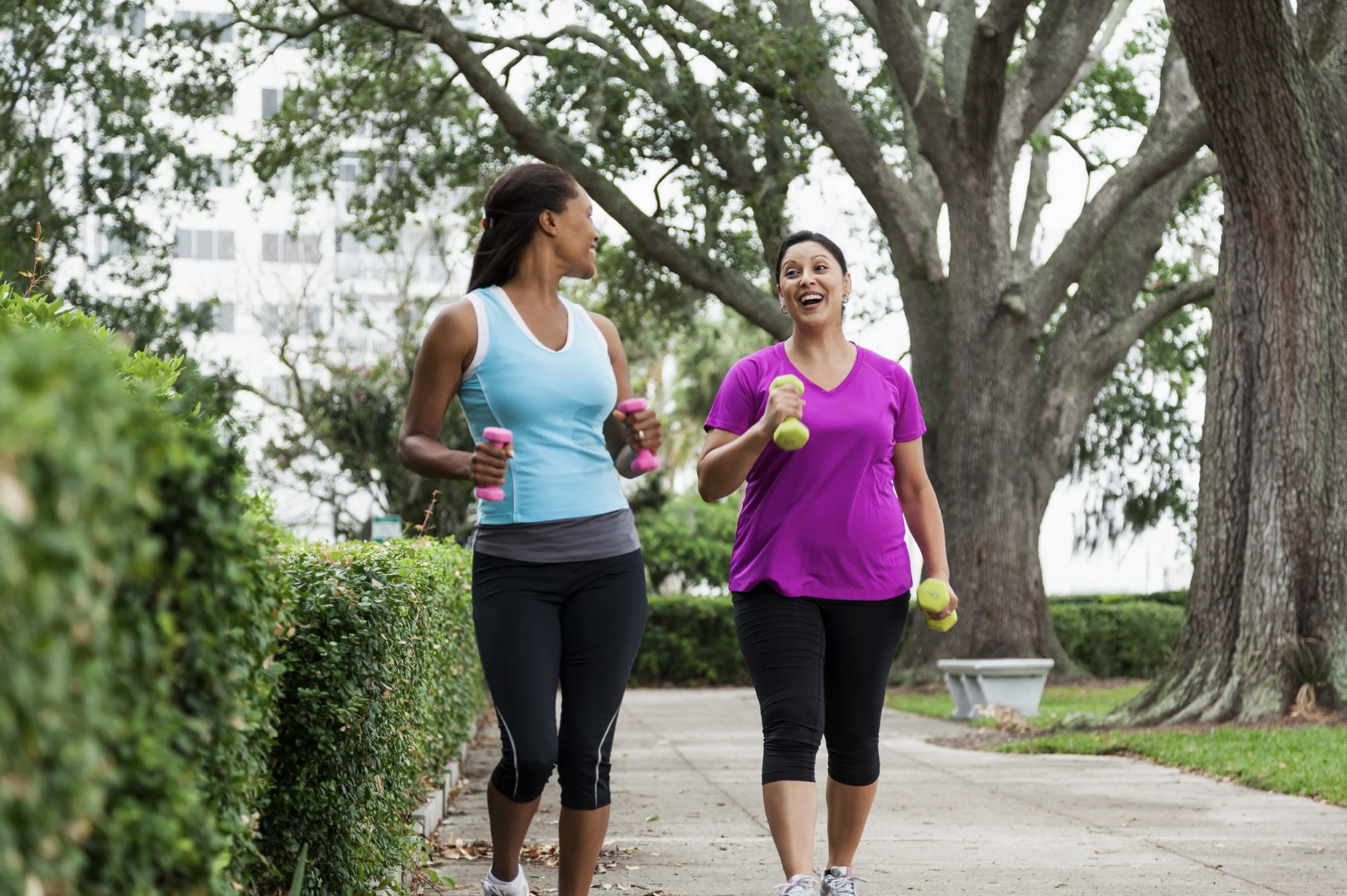

Your daily habits, lifestyle choices, and dietary patterns can all influence how your body manages dopamine—a neurotransmitter (chemical messenger that promotes communication between nerves). This crucial brain chemical helps regulate muscle movement and contributes to positive feedback that gives an emotional sense of satisfaction and contentment. 1. Eat a Balanced, Protein-Rich Diet Proper nutrition plays… read on >






























-300x211.jpeg)

